
Sludge separation − filtration
Filtration theory defines the way in which water flows through the bed, which is formed of the sludge solids (cake)
Your web browser is out of date.
Update your browser for better security, speed and to get the best experience on this website.
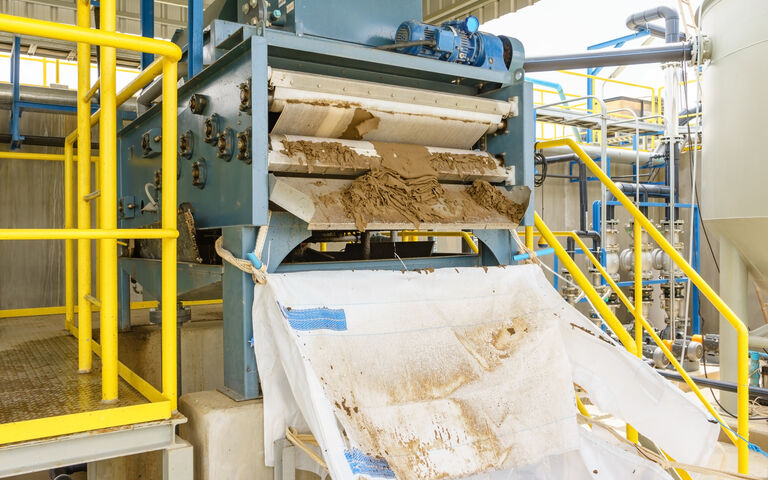
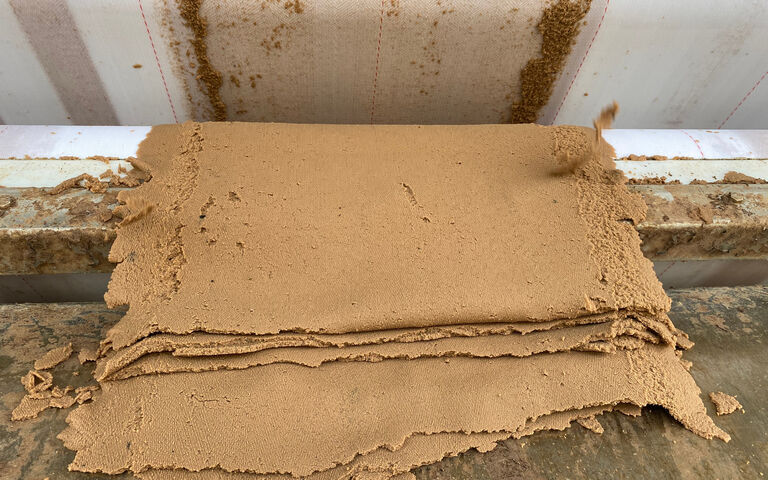
A rotary press dewaters sludge using a cylindrical vessel housing two slowly-rotating (at < 2 RPM) circular permeable screens which are sandwiched together. The sludge enters the channel formed between the two screens and follows a circular path around the channel at a small applied pressure, the water (or filtrate) passing through the screen as the sludge passes along the channel.

Filtration theory defines the way in which water flows through the bed, which is formed of the sludge solids (cake)

An overview of sludge dewatering − an introduction to sludge dewatering theory and technologies
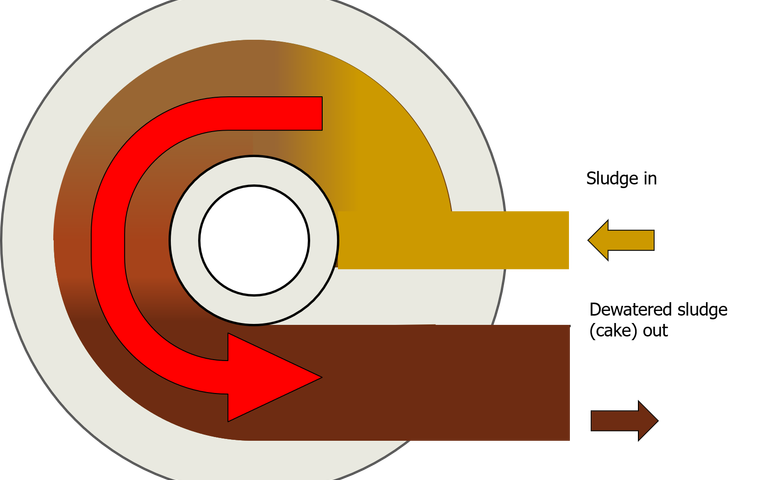
This technology removes water by passing the sludge through a narrow, rotating parallel-flow channel with porous walls
Sludge solids separation theory − a brief introduction to the theories around sludge sedimentation, cake filtration and cake compression.
A belt filter press (BFP) dewaters sludge by pressing it between two revolving permeable belts to squeeze out the water
Centrifugal dewatering consolidates sludge by encouraging particles to migrate to the walls of a rapidly rotating cyclinder
Drying beds dewater sludge by allowing the liquid to both drain from the sludge under gravity and evaporate from its surface
A filter press dewaters sludge by pressing it between a series of porous plates at high pressure to squeeze out the water
A lagoon is a large shallow reservoir filled with sludge, which settles and stabilises over an extended time period
A screw press dewaters sludge by passing it along the inside of an inclined permeable cylinder using an Archimedean screw
Conditioning is the pretreatment of sludge upstream of thickening and dewatering to promote solid-liquid separation
Thickening processes concentrate the sludge by removing part of the free water, such that the product can still be pumped
Dewatering processes mechanically remove a significant proportion of the sludge water to produce a 15-45% cake product
In sludge drying the sludge moisture is removed as water vapour by heating, generating a pelleted or powdered product
Sludge stabilisation − alkaline stabilisation, lime and solids dosing, plus anaerobic and aerobic digestion
Thermochemical methods are used to either significantly reduce the sludge solids content or pre-treat sludge upstream of AD
Sludge is the main waste stream from the treatment of wastewater