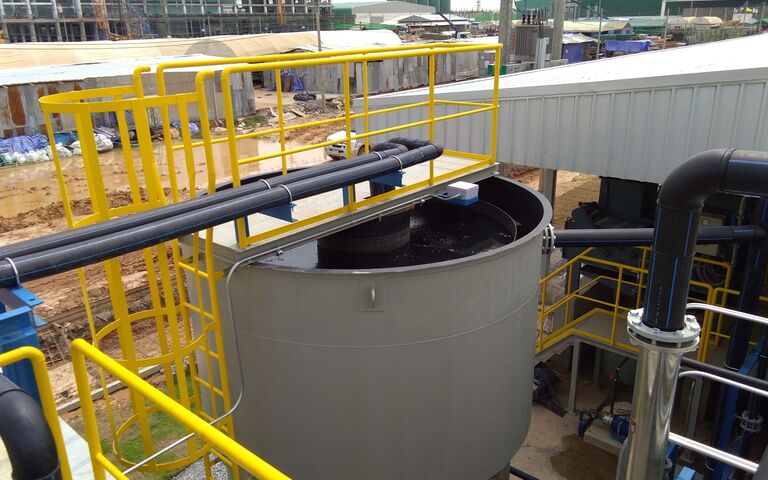

Sludge separation − gravitation/sedimentation
Gravitation (sedimentation or settlement) is the separation of particles from water on the basis of their weight
Your web browser is out of date.
Update your browser for better security, speed and to get the best experience on this website.
Sludge drying refers to processes where moisture is removed from sludge as water vapour. These processes often require pre-treatment ('conditioning'). With sludge thickening or dewatering, moisture is removed as a liquid.

Gravitation (sedimentation or settlement) is the separation of particles from water on the basis of their weight

The theory of centrifugation relates to sedimentation theory as it acts to enhance gravity through the centrifugal force
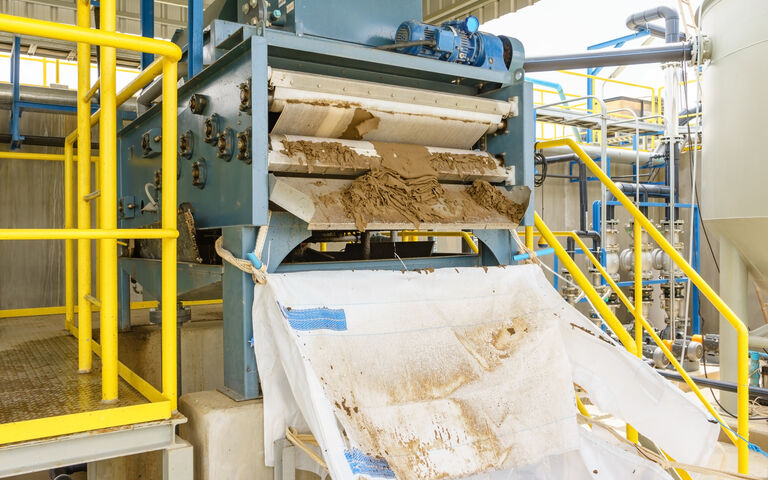

Filtration theory defines the way in which water flows through the bed, which is formed of the sludge solids (cake)

An overview of sludge conditioning − chemical and thermal
Thickening and dewatering processes often need pre-treatment (conditioning) to help separate the water from the solids

The chemical pre-treatment of sludge helps remove water upstream of thickening and dewatering processes

Thermal processes are used to condition sludges upstream of anaerobic digestion as well as pre-treating sludge for dewatering
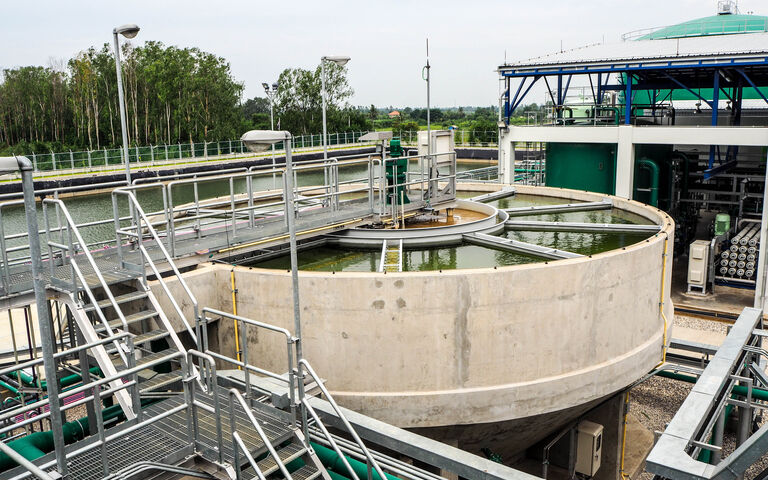

An overview of sludge thickening − an introduction to theory and related technologies

Processes which act to remove water from the sludge to reduce its volume are called thickening and dewatering

Gravity thickening increases the solids concentration by allowing the particles to settle to the base of a vessel

Dissolved air flotation thickens the sludge by encouraging solids to float to the surface by attaching to rising air bubbles

GBT thickens the sludge by allowing the water to drain from the sludge under gravity through a permeable moving belt

Rotary drum thickening thickens the sludge by agitating the solids in a slowly-rotating vessel with porous walls

Sludge concentration increases as particles are encouraged to migrate to the walls of a rapidly rotating cylindrical vessel
Other processes include membrane thickening − water is extracted through a membrane, increasing the solids concentration

An overview of sludge dewatering − an introduction to sludge dewatering theory and technologies

Dewatering processes provide a concentrated, consolidated product along with a diluted stream which is predominantly water

These presses dewater sludges to produce a cake with a dry solids content of 30% or more in the case of primary sludge

A screw press is a dewatering technology based on a slowly-rotating (~5 RPM) Archimedean screw within a cylindrical screen
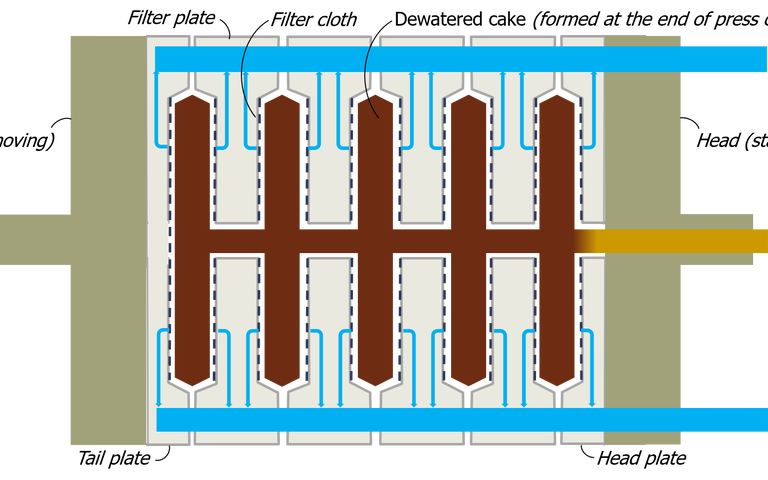
The filter press forces water from the sludge by applying high pressures to sludge layers held between rectangular plates
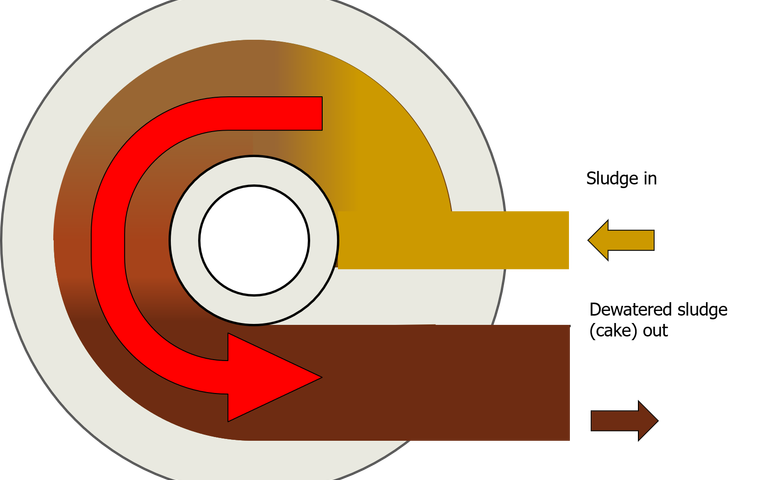
This technology removes water by passing the sludge through a narrow, rotating parallel-flow channel with porous walls

Centrifugation is used for thickening and dewatering sewage sludge − dewatered sludge has a higher dry solids concentration

Drying beds dewater sludge by allowing the liquid to drain and to evaporate. Lagoons provide dewatering through evaporation
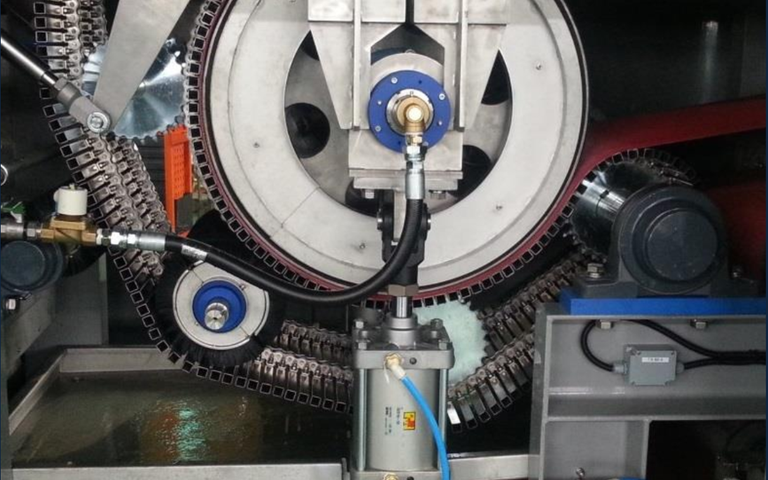
Electro-dewatering technology provides enhanced removal by non-mechanical means through the application of an electric field
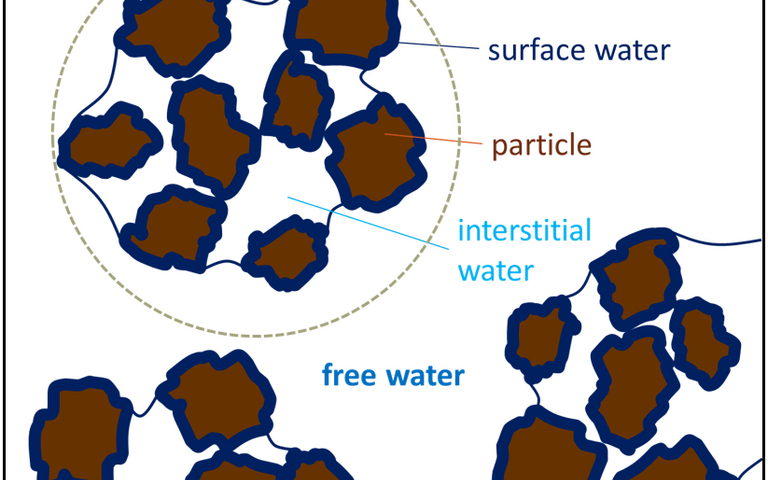
An overview of sludge drying − an introduction to sludge drying theory and technologies
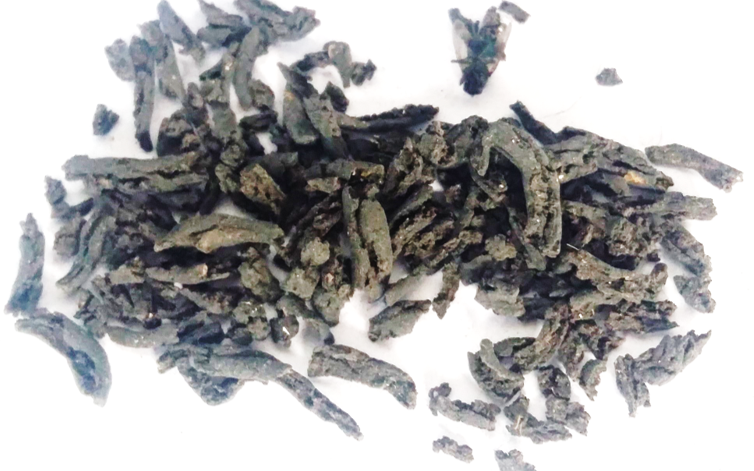

Processes where moisture is removed from sludge as water vapour are known as 'sludge drying'

When sludge dries, it goes through three different phases as the water evaporates

Sludge drying processes operate at solids temperatures of 60-93 °C to encourage water to evaporate and leave a solid residue

Sludge drying processes are generally configured as convective, conductive, or as solar dryers

Conductive drying indirectly heats sludge by bringing the sludge particles into contact with an externally-heated surface

Convective sludge dryers are the most commonly used type of dryer for sewage sludge

Solar dryers make use of renewable solar energy to dry sludge and need a larger footprint to allow for increased drying times
Animation to demonstrate the operating process of the Alfa Laval AS-H G3 belt press for sludge dewatering. This belt press can handle high volumes, and is used in both municipal and industrial wastewater treatment.
Conditioning is the pretreatment of sludge upstream of thickening and dewatering to promote solid-liquid separation
Thickening processes concentrate the sludge by removing part of the free water, such that the product can still be pumped
Dewatering processes mechanically remove a significant proportion of the sludge water to produce a 15-45% cake product
In sludge drying the sludge moisture is removed as water vapour by heating, generating a pelleted or powdered product
Conditioning is the pretreatment of sludge upstream of thickening and dewatering to promote solid-liquid separation
Thickening processes concentrate the sludge by removing part of the free water, such that the product can still be pumped
Dewatering processes mechanically remove a significant proportion of the sludge water to produce a 15-45% cake product
In sludge drying the sludge moisture is removed as water vapour by heating, generating a pelleted or powdered product
Sludge stabilisation − alkaline stabilisation, lime and solids dosing, plus anaerobic and aerobic digestion
Thermochemical methods are used to either significantly reduce the sludge solids content or pre-treat sludge upstream of AD
Sludge is the main waste stream from the treatment of wastewater