
Sludge thermochemical treatment
An introduction to sludge thermochemical treatment methods
Your web browser is out of date.
Update your browser for better security, speed and to get the best experience on this website.
Supercritical water oxidation (SCWO) refers to the rapid oxidation of organics in water in the supercritical phase of water. 'Supercritical’ refers to the state of water within a specific region of pressure (>218 bar) and temperature (>374 °C) where water becomes both a solvent and oxidant for all chemical species.

An introduction to sludge thermochemical treatment methods
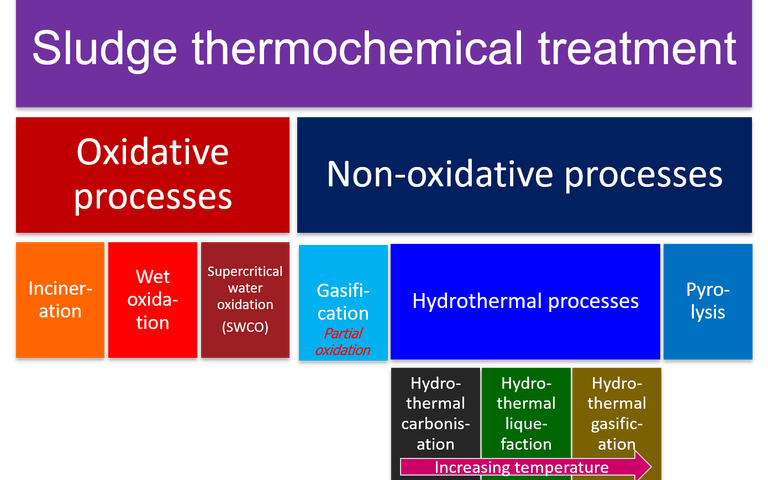
Thermochemical methods are used for either degrading the sludge solids or pre-treating sludge upstream of anaerobic digestion
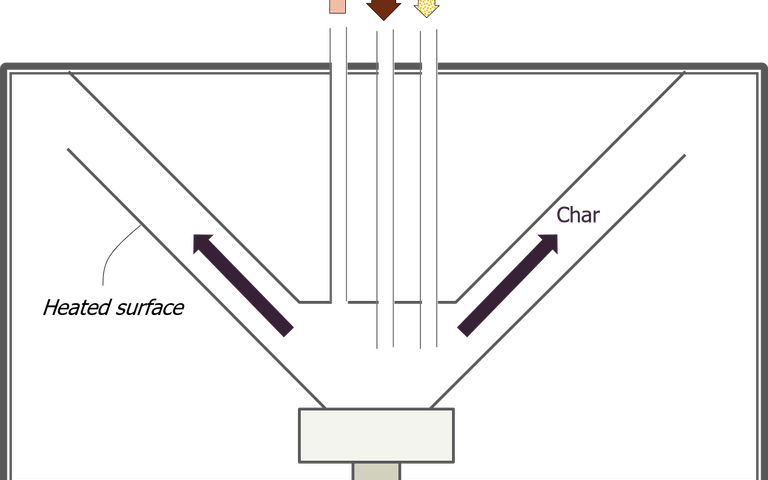
Various reactor configurations exist for sludge thermochemical treatment which vary in design, operation and application

An introduction to oxidative sludge thermochemical treatment methods
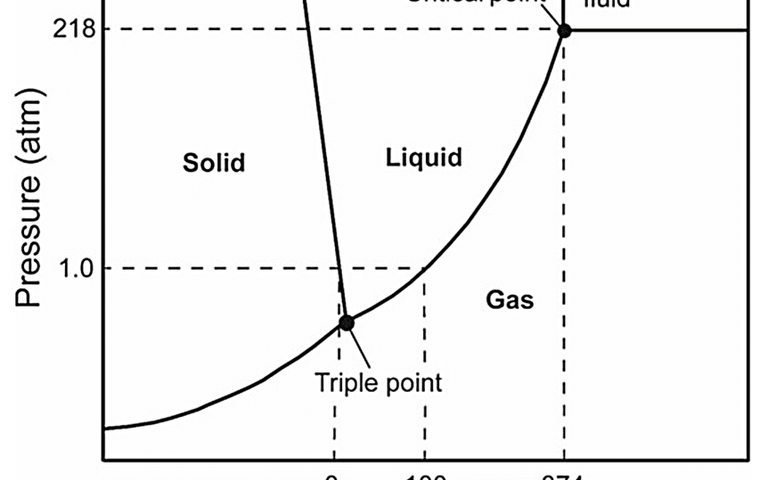
Supercritical water oxidation refers to the oxidation of organics in water in the so-called supercritical phase of water
Oxidative methods for sludge thermal treatment comprise incineration, wet air oxidation and supercritical water oxidation
Non-oxidative thermochemical treatment of sewage sludge refers to treatment at elevated temperatures in the absence of oxygen
Thickening, dewatering and drying extract water from sludge to reduce the sludge volume
Sludge stabilisation − alkaline stabilisation, lime and solids dosing, plus anaerobic and aerobic digestion
Sludge is the main waste stream from the treatment of wastewater