
Sludge stabilisation
An overview of sludge stabilisation − alkaline stabilisation, lime and solids dosing, plus anaerobic and aerobic digestion
Your web browser is out of date.
Update your browser for better security, speed and to get the best experience on this website.
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is the most extensively employed sludge stabilisation process. AD stabilises the sludge biologically in the absence of air. In doing so, it reduces the amount of volatile solids by their conversion to a biogas (methane CH4, carbon dioxide CO2 and water H2O). The biogas then demands further processing for recovery and reuse of its methane content.

An overview of sludge stabilisation − alkaline stabilisation, lime and solids dosing, plus anaerobic and aerobic digestion
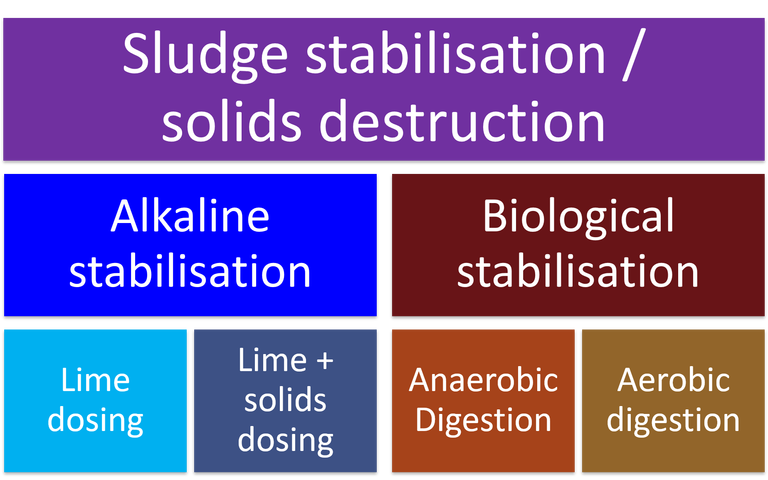
Stabilisation processes reduce the odour and putrescence of sludge, and level of pathogenic organisms

An overview of anaerobic digestion − an introduction to sludge processing AD theory

Anaerobic digestion (AD) is the most extensively employed sludge stabilisation process, and generates a methane gas product
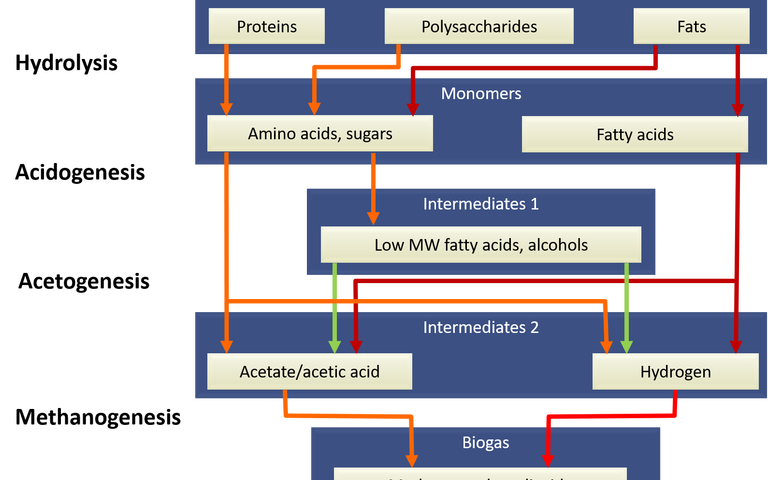
Anaerobic digestion is a multi-step biochemical process comprising hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis

Anaerobic digestion can be a single or multiple tank process, and employ different conditions of stirring and temperature

Pretreating sludge upstream of the anaerobic digestion is sometimes carried out to improve the sludge biological treatability

Anaerobic digestion can be conducted at moderate (mesophilic) or elevated (thermophilic) temperature conditions

Two widely recognised operational challenges to anaerobic digestion operation are foaming and over-acidification
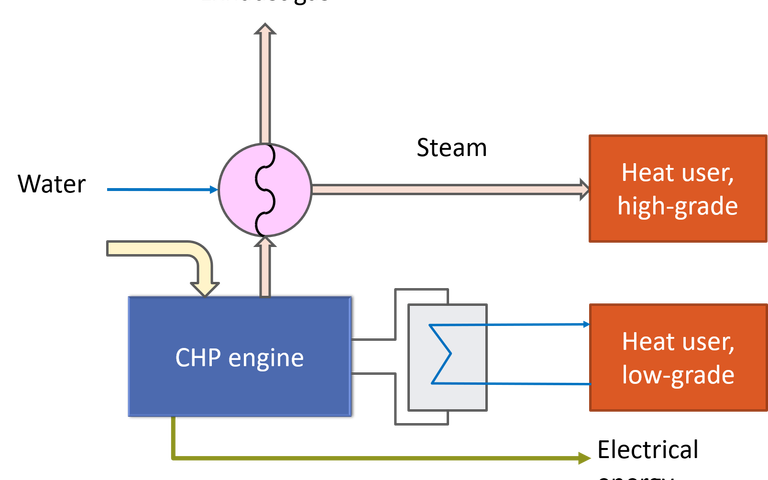
Anaerobic digestion generates a biogas containing 50-60% methane which can be used to generate heat and electrical power

The digestate is the residual slurry, containing up to 20% solids, generated from the anaerobic digestion process
The supernatant is the liquid stream generated from anaerobic digestion process and has a high nutrient content
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is the most extensively employed sludge stabilisation process and, as with most sludge and wastewater unit processes, the design and performance of AD depends on the feed characteristics. Professor Simon Judd explains.
Alkaline stabilisation reduces the sludge odour, putrescence and pathogenic organism content by raising its pH using lime
AD stabilises the sludge biologically in the absence of air, producing a useful biogas while biodegrading the organic solids
Aerobic digestion is the degradation of the organic sludge solids to carbon dioxide in the presence of oxygen
Thickening, dewatering and drying extract water from sludge to reduce the sludge volume
Thermochemical methods are used to either significantly reduce the sludge solids content or pre-treat sludge upstream of AD
Sludge is the main waste stream from the treatment of wastewater