
Sludge stabilisation
An overview of sludge stabilisation − alkaline stabilisation, lime and solids dosing, plus anaerobic and aerobic digestion
Your web browser is out of date.
Update your browser for better security, speed and to get the best experience on this website.
Aerobic digestion is the degradation of the organic sludge solids in the presence of oxygen. The oxygen is introduced as fine bubbles of air into the reactor. The micro-organisms in the sludge convert the organic material to carbon dioxide and water, and the ammonia and amino species to nitrate. Aerobic digestion resembles the conventional activated sludge (CAS) process but excludes a wastewater feed and employs longer solids retention times.

An overview of sludge stabilisation − alkaline stabilisation, lime and solids dosing, plus anaerobic and aerobic digestion
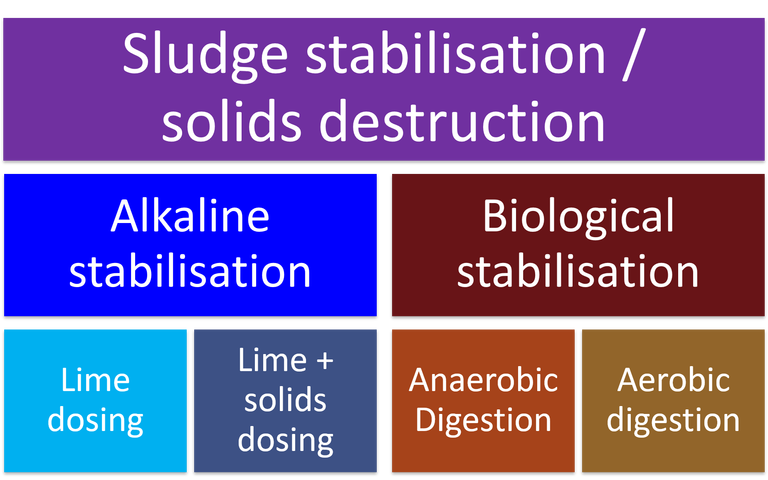
Stabilisation processes reduce the odour and putrescence of sludge, and level of pathogenic organisms

An overview of aerobic digestion and sludge composting

Aerobic digestion is the degradation of the organic sludge solids in the presence of oxygen

Composting is a type of aerobic digestion. The most established method for composting is through the use of windrows
Aerobic wastewater treatment with classical activated sludge. A taster for Judd Water & Wastewater Consultants' 'MBR Insights' training package, in this video Simon Judd explains classical aerobic wastewater treatment.
Alkaline stabilisation reduces the sludge odour, putrescence and pathogenic organism content by raising its pH using lime
AD stabilises the sludge biologically in the absence of air, producing a useful biogas while biodegrading the organic solids
Alkaline stabilisation reduces the sludge odour, putrescence and pathogenic organism content by raising its pH using lime
AD stabilises the sludge biologically in the absence of air, producing a useful biogas while biodegrading the organic solids
Aerobic digestion is the degradation of the organic sludge solids to carbon dioxide in the presence of oxygen
Thickening, dewatering and drying extract water from sludge to reduce the sludge volume
Thermochemical methods are used to either significantly reduce the sludge solids content or pre-treat sludge upstream of AD
Sludge is the main waste stream from the treatment of wastewater