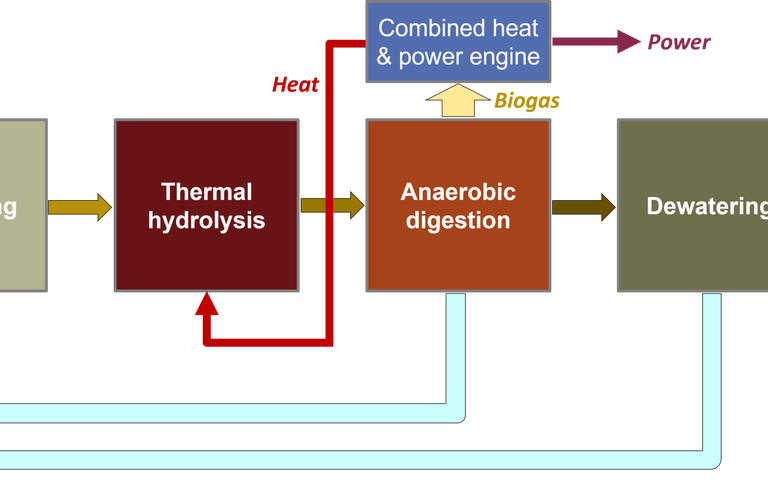
Managing anaerobic digestion digestate in sludge treatment

Managing AD digestate
The digestate is the residual slurry, containing up to 20% solids, generated from the anaerobic digestion (AD) process. It is usually rich in nutrients such as ammonia and phosphates as well as micronutrient metals. Its primary use is as a soil conditioner, subject to its meeting regulatory standards regarding toxic metals content.
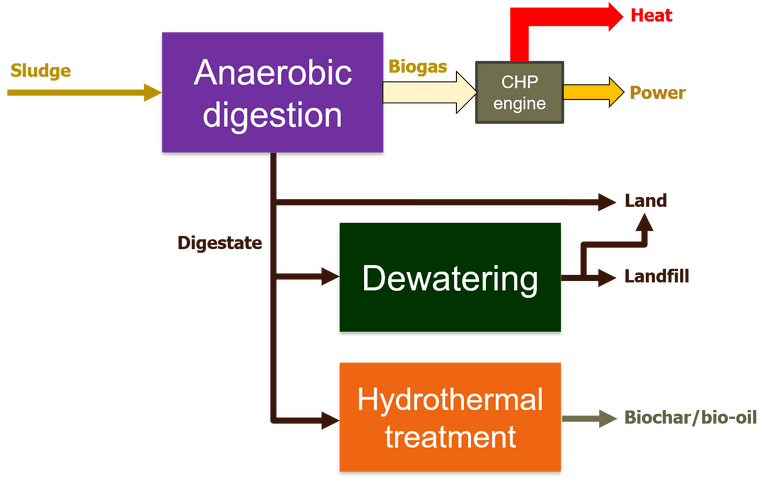
If the digestate metals content is too high to allow it to be applied to soil then further treatment is required, or else alternative end disposal options, such as landfilling, explored. If landfilling is the intended disposal route then concentration of the solids by thickening and/or dewatering is usually carried out to reduce the sludge volume, and thus the disposal cost. The water-soluble nutrients may then be recovered from the liquid stream from these solid−liquid separation processes.
Other processing options have been explored for recovering resources from digestate, including hydrothermal treatment. These processes recover the latent energy from the digestate, related to its carbon content.